Principle of Ultrasonic Welding
- TOP
- Ultrasonic Welding
- Principle of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding is a joining method in which ultrasonic vibration is applied to workpieces made of thermoplastic resin while applying pressure, causing the workpieces to melt.
Ultrasonic welding melts the resin in less than one second, enabling high-speed joining.
It is also an environmentally friendly joining method because it does not use adhesives or solvents.
Ultrasonic welding is used in variety of applications, including welding molded products, boss caulking, and sealing films and non-woven fabrics.
Basic Configuration of Ultrasonic Welder and Role of Each Part
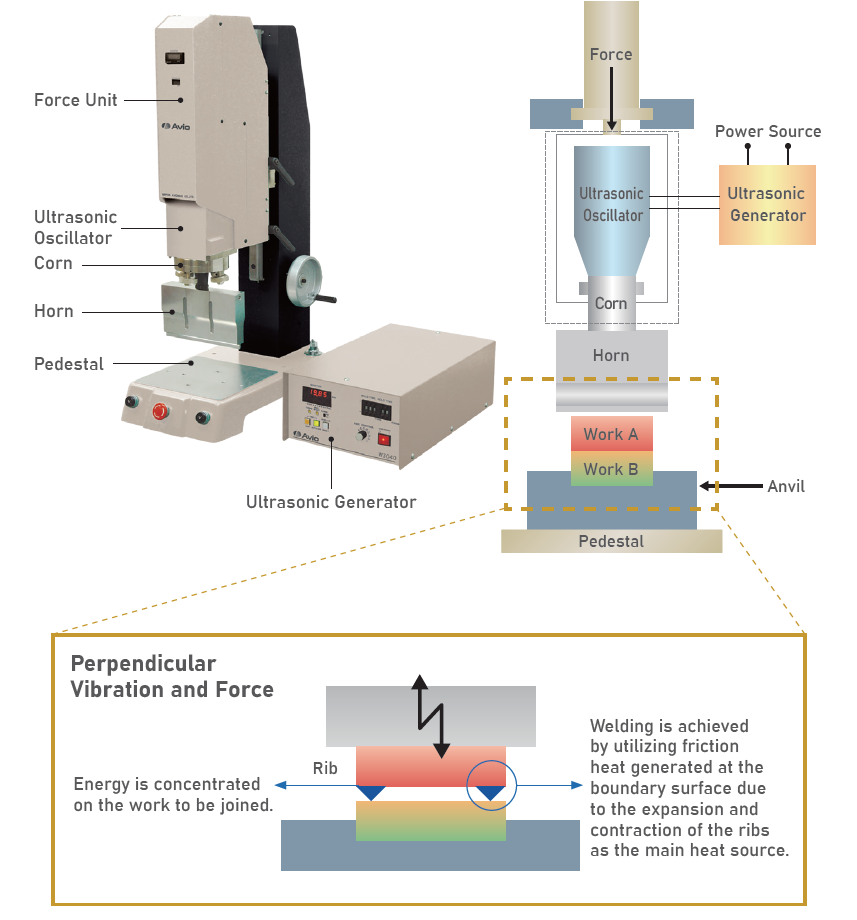
By applying ultrasonic vibration and force to the object to be joined, welding is achieved by utilizing the heat generated at the boundary surface of the objects.
- Ultrasonic Generator: A commercial power line frequency (50/60 Hz) source is converted to high electrical frequencies of ultrasonic range or higher
- Ultrasonic Transducer & Cone: Converts electrical frequency to a mechanical vibrational frequency and amplitude
- Horn: Resonates with the vibration of the transducer, vibration, applies force to the objects to be joined, and directs energy to the area to be joined
- Anvil (Support Jig): It is used to position and fix the object to be joined so that the vibration energy will not be wasted.
- Rib: It helps to direct and concentrate the energy at the joined section
Rib Shape and Knurling of Horn
It is common to provide ribs. In case ribs cannot be provided, such as the case of a thin material, knurling may be applied to the horn.
Rib Shape
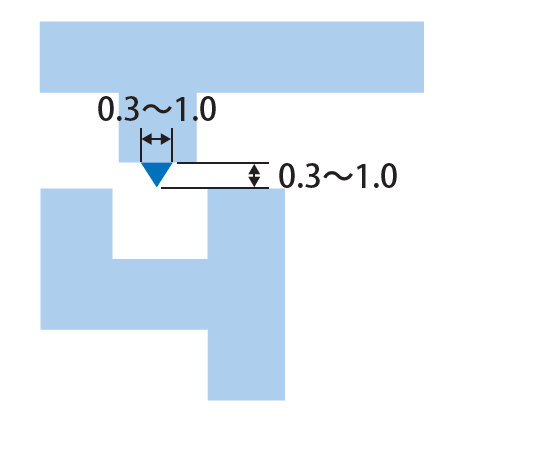
(1) Standard Type
Most Frequently Used Model
(2) Step Joint
Positioning is Easy
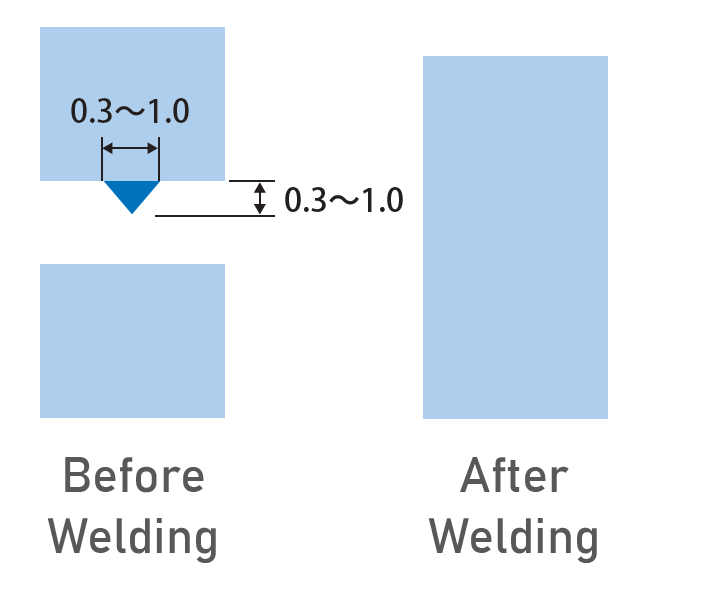
(3) Share Joint
Airtight Welding of POM, PP and PBT
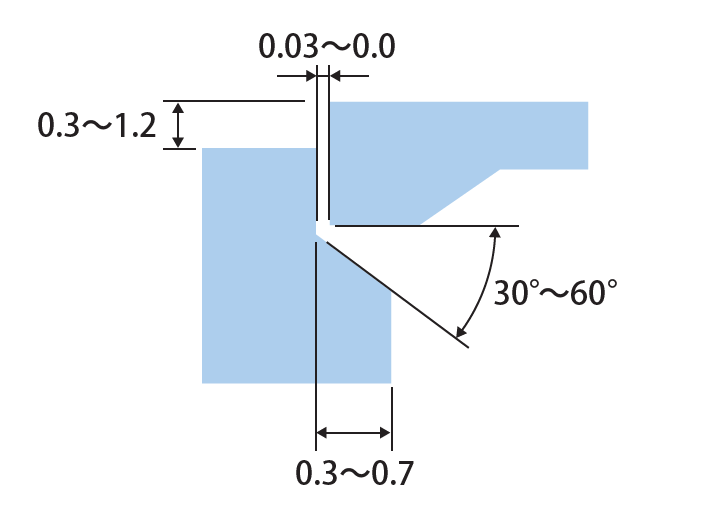
(4) Tank Joint
Prevention from Extending Out of Burr
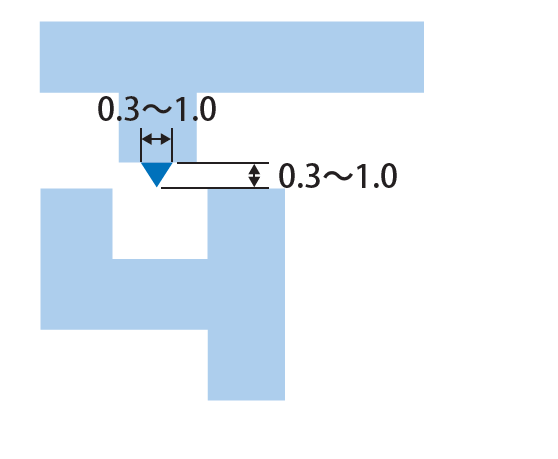
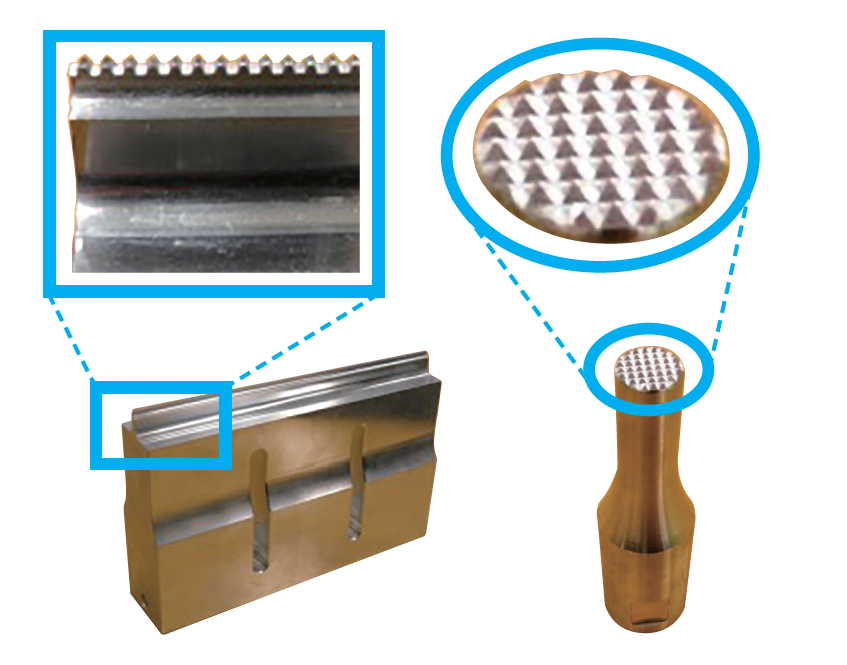
Knurling of Horn
We offer knurling of various shapes in order to achieve the finish according to the purpose of welding strength and design of customer’s requirements.

 Resistance Welding
Resistance Welding Hot Bar Reflow Soldering
Hot Bar Reflow Soldering Ultrasonic Metal Welding
Ultrasonic Metal Welding Parallel Seam
Parallel Seam  High Frequency Induction Heating
High Frequency Induction Heating